
The Case of Short-wave Infrared Imagery
The utilisation of advanced imaging techniques has revolutionised the ability to perceive and understand the world from afar. Hyperspectral imagery stands a head above with its unparalleled capacity to capture detailed information across the electromagnetic spectrum. Within this spectrum, the Short-Wave Infrared band emerges as a crucial section that offers unique insights into various phenomena that are otherwise challenging to observe.
Hyperspectral Imagery and Its Channels
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a broad range of wavelengths, divided into distinct channels essential for remote sensing applications. These channels include Ultraviolet, Visible, Infrared, and Microwave, each offering unique insights into the environment. In hyperspectral imaging, data is collected across numerous spectral bands within these channels, enabling detailed analysis of materials and phenomena.
The Infrared channel is further broken down to Near-Infrared (NIR), Short-wave Infrared (SWIR), Middle-wave Infrared (MWIR), and Long-wave Infrared (LWIR) channels. These sub-divisions facilitate targeted observation and analysis of specific features, such as moisture content, mineral composition, and thermal characteristics.
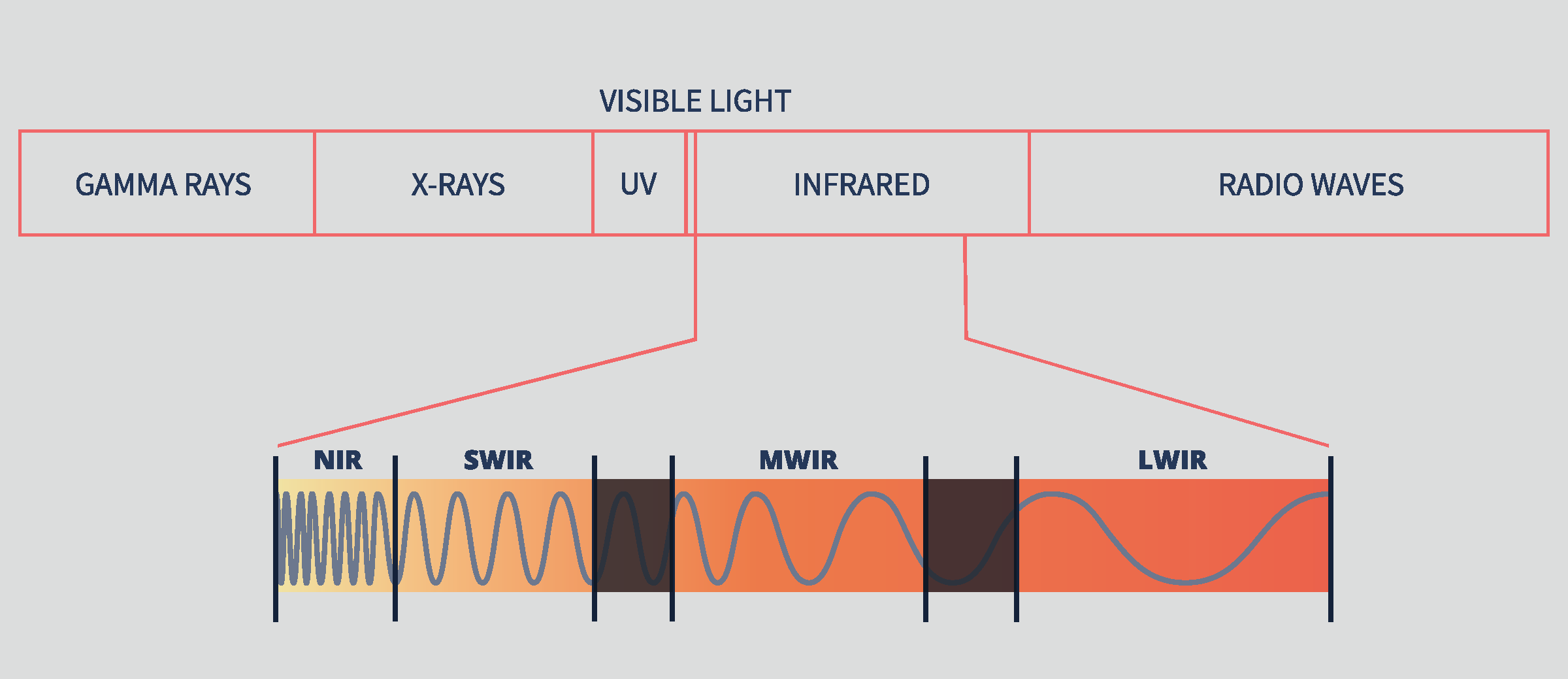
Each spectral channel captures distinct information, contributing to a comprehensive characterization of the observed scene. The NIR region, for instance, is sensitive to vegetation health and soil properties, while the SWIR band excels in material identification and moisture detection. Depending on the application, different channels are prioritised to extract relevant information effectively.
The Importance of SWIR Region
The SWIR region offers great insights across a diverse array of applications. Spanning approximately 1,400 to 2,500 nanometers in wavelength, the region’s unique spectral characteristics make it an invaluable tool for material identification, environmental monitoring, and disaster response.
Mineral exploration benefits significantly from its capabilities, enabling users to distinguish between various rock types and mineral compositions. SWIR imagery captures surface data which can provide invaluable insights into potential subsurface mineral deposits and geological formations. This aids in resource exploration and extraction planning, guiding the strategic allocation of resources and investment in mining ventures.
SWIR’s sensitivity to subtle changes in vegetation health and moisture content makes it indispensable for wildfire response efforts and precision agriculture. One of the region’s distinguishing features is its significant absorption by water and water vapour, leading to bands of absorption at specific wavelengths. Its sensitivity to moisture correlates with critical metrics such as leaf water content, plant water stress, and forest fire burn severity.
SWIR aids in early detection and mitigation strategies by detecting early signs of fire hazards, such as dry vegetation or moisture anomalies. It ultimately can help in reducing the risk and impact of wildfires. The agricultural sector can also benefit from SWIR for ensuring food security. By assessing crop health and moisture levels, SWIR imagery enables informed agricultural management decisions, leading to optimised yields and resource utilisation.
Technical Advantages of SWIR
Unlike other regions in the electromagnetic spectrum, SWIR can penetrate through challenging atmospheric conditions, including smog, clouds, and haze. This unique capability ensures clear imagery even in adverse weather scenarios, making SWIR indispensable for disaster management, oil spill detection, and snow and ice discrimination.
Moreover, SWIR sensors demonstrate minimal scattering effects, resulting in superior image quality and enhanced visibility of features amidst challenging environmental conditions. This inherent advantage allows for precise analysis and interpretation of remote sensing data, even in areas prone to atmospheric interference.
The spectral sensitivity of SWIR to moisture further enhances its utility, enabling the assessment of critical environmental parameters such as vegetation health and soil moisture levels. By capturing subtle variations in moisture content, SWIR sensors contribute to a comprehensive understanding of ecosystem dynamics and facilitate informed decision-making in fields ranging from agriculture to conservation.
Additionally, SWIR has the ability to differentiate between objects with similar colours in the visible spectrum. It can provide tactical advantages in remote sensing applications. This capability enhances object recognition and classification, thereby improving the accuracy and reliability of remote sensing analyses.
Esper’s Edge in Hyperspectral Imaging
Esper is at the forefront of this advancement, offering access to hyperspectral data captured across the electromagnetic spectrum through its state-of-the-art sensors. By harnessing the unique capabilities of SWIR and other spectral bands, Esper is steadfast in its commitment to delivering accessible and actionable data to support a diverse array of use cases.
What sets Esper apart from its competitors is its adept utilisation of SWIR, enabling improved image quality and enhanced visualisation even in the face of challenging environmental conditions. The inclusion of SWIR represents a significant leap forward in our ability to comprehend and interact with the Earth's surface and atmosphere. Its remarkable versatility spans applications from mineral exploration to disaster response, underscoring its indispensable role in modern remote sensing. SWIR unlocks unique insights that are simply unattainable in other electromagnetic fields, providing a crucial edge in remote sensing endeavours.
Esper remains steadfast in its dedication to pushing the boundaries of technology and driving innovation in remote sensing. Through ongoing research, development, and collaboration, Esper aspires to unlock new frontiers and solutions that benefit society and our planet as a whole.
As part of our commitment to democratising access to hyperspectral data, Esper's EarthTones data platform offers a user-friendly interface for seamless exploration, analysis, and insights derived from spectral data. Whether it's pinpointing mineral deposits, monitoring vegetation health, or responding to environmental crises, Esper's data platform empowers users to leverage hyperspectral data tailored to their specific needs. Learn more about EarthTones here.
Esper is gearing up for its next mission launch, poised to continue leading the charge in advancing hyperspectral remote sensing capabilities. Join us as we embark on the next phase of exploration and innovation, shaping a brighter future for remote sensing and beyond.